Acute pain in the lumbar region, against the background of osteochondrosis of the spine, is a widespread problem that the vast majority of people face. Getting to us "as a reward" for our straightforwardness (due to increasing the axial load on the spinal column), this ailment sooner or later affects each resident of the planet, the only question is how quickly this happens, and how expressed the symptoms. Therefore, the issue of treatment of spine osteochondrosis is a very relevant topic.

So what is osteochondrosis? Consider briefly how the development of the disease occurs. In its very name, if you translate it from Latin literally, the structures that change with osteochondrosis are determined: bone and cartilage. In order to depreciate and resistance to vertical loads, nature placed in between our vertebrae a peculiar fibrous-chryshot "pillows"-intervertebral discs. Their nutrition is carried out in childhood due to blood vessels, which are lost by approximately 25 years, and nutrition begins to be diffusely due to the surrounding muscles.
In pathological loads on the spinal column (sedentary work, or vice versa - excessive physical activity), violations of the processes of the mineral metabolism, the intervertebral disc loses its elastic and amortizing properties, its height decreases, the structure of the vertebrae changes, pathological bone growths (osteophytes and cloth plate) are changed, mobility is disturbed. The affected area of the spine. In the late stages of the disease, the central part of the intervertebral disc, the so -called jacket nucleus, breaking through the fibrous ring, forms a kind of bag of protrusion between the bodies of the vertebrae - the intervertebral hernia. A hernia can cause compression of nerve roots adjacent to the vertebrae, intense pain occurs in the compression zone, as well as in the area regulated by the affected nerve. Due to the constant irritation of nervous plexus, a reflex spasm of skeletal muscles occurs, called a protective defense in medicine, which on the one hand protects the suffering section of the spine from excessive movements, and on the other hand, enhances compression, edema and pain in the affected area. In the vast majority of cases (90%) pain with osteochondrosis (even extremely pronounced) is due to muscle spasm! In other cases, the cause of pain is the compression of the nerve root or spinal cord directly by the hernia of the intervertebral disc.
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine: how to treat
Of all the parts of the spine, and in total there are five of them (cervical, chest, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal), due to the greatest motor load, the lumbar most often suffers from the manifestations of the disease. Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine has bright symptoms familiar to everyone, and its treatment is a significant social task, since it worsens the quality of life of not only elderly people, but also active people of working age.
Pain can be localized directly in the lumbar region, as well as on the front surface of the thigh, or along the entire posterior or outer surface of the leg, sometimes to the very fingers. Often, pain is given to the gluteal region, sacrum, crotch, and sometimes they can only be localized in these areas, disguised as diseases of the genitourinary sphere and intestines and making it difficult to produce the correct diagnosis. The intensity of the pain syndrome can be so high that a person loses the ability to make the most elementary movements, takes forced poses and loses normal sleep. This is just the same radicolite, which in wide circles has long become a synonym for the disease itself.
Limiting motor activity. The usual movements and sensitivity in the limbs are violated, muscle convulsions, paresthesia (sensations of tingling, burning "crawling goosebumps") occur. Violation of the function of the pelvic organs. With intense radicular syndrome, known to everyone as radicolite, or with massive hernial protrusion, urination and intestinal work may even be disturbed, causing severe torment in the patient.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine often becomes a difficult task for both the patient and the doctor. Each person suffering from this ailment was asked by questions: "How to treat osteochondrosis of the lower back? ", "How to treat osteochondrosis of the lumbar region? ", "If treatment of osteochondrosis of the lumbar department at home does not help - which doctor to contact? ", "If tablets and ointments do not help with lumbar osteochondrosis - how to treat? ". The following doctors will help exacerbation of osteochondrosis and prescribe competent treatment: therapist, neurologist, medical massage specialist, manual therapist, physiotherapist, and, if necessary, surgical treatment is a neurosurgery.
Ways to combat osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
The main thing in the treatment of osteochondrosis is the right lifestyle! In people who are actively and correctly involved in physical culture and monitor the spine, the back never hurts! Unfortunately, few people follow these simple truths.
By analyzing this issue, you can highlight:
- medication;
- Non -drug.
Non -drug methods for the treatment of pathology of the lumbar spine
Distracting procedures. Their effect lies in the name itself - the use of various applicators, massage rugs and rollers, woolen belts, "lotions" and "rubbing" due to the effects on the surface nerve endings and blood vessels slightly reduces muscle spasm and pain syndrome. These methods can be used as auxiliary, but isolated use for exacerbation of osteochondrosis of the lumbar region without systemic treatment with special drugs is ineffective.

Immobilization means. These means are understood as bandages of various designs, the wearing of which allows you to protect the spine from sudden and "dangerous" movements and redistribute the load during static work. Immobilization means can be purchased in stores of medical equipment and pharmacies, however, before buying it is advisable to consult a doctor who will help determine the optimal design, rigidity and completion of the bandage in your situation. It is advisable to use them only for the time of exposure to adverse factors (trips by the wheel, sedentary work, etc. ), since prolonged use causes muscle hypotrophy.
Medical physical education (exercise therapy) - An integral component of complex treatment of osteochondrosis. Performing exercises aimed at maintaining the tone of the frame muscles of the back and removing pathological muscle spasm help restore and maintain motor activity, reduce the intensity of the pain syndrome. A significant plus of exercise therapy is that after training by the instructor, a person can independently perform exercises at home daily, as well as in the existence of a set of exercises applicable even with an exacerbation of the process. The most effective method of exercise therapy is mechanotherapy - classes on simulators according to an individually developed method, since the formation of muscle corset needs work with weights.
Acupuncture. Based on the results of recent studies, the use of this method of methodology popular in broad circles is considered evidence -based medicine unreasonable for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine that does not eliminate the symptoms of the disease, and refers to non -traditional treatment methods.
Physiotherapy, included in national clinical recommendations and standards for the provision of medical care for osteochondrosis, has long proved its effectiveness in the treatment of this disease. With osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, electromyostimulation, amplipulse therapy, shock-wave therapy, intracamous myostimuration, laser therapy are used. Magnetotherapy remains the popular method in complex treatment. Its advantages include good tolerance and a small list of contraindications, the possibility of use in the acute period of the disease. Acting on all links of the pathological process, after several procedures it significantly reduces the pain and allows a person to expand motor activity. In addition, by improving the trophism of affected tissues, it slows down the progression of the disease. An unconditional advantage of this method is the possibility of its independent use by the patient outside the walls of a medical institution. But if all of the above non -drug methods were ineffective - how then to treat lumbar osteochondrosis?
Drug treatment
Diseases involve the appointment of the following medicinal groups:
Non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) They are produced in forms both for local (gels, ointments, cream), and for systemic use (tablets, candles, solutions for intramuscular and intravenous administration). Their action is based on blocking the inflammatory process at an enzymatic level, as a result of which edema in the lesion zone is eliminated and the pain syndrome is significantly reduced.
In the early stages of the disease, there are enough local use of NSAIDs in combination with non -valley methods (therapeutic exercises, magnetotherapy). With a pronounced pathological process and intensive pain, you have to resort to tablet and sometimes injectable forms of drugs. Unfortunately, possessing good anti-inflammatory and painkillers of NSAIDs, with prolonged systemic use, can cause the development and exacerbation of ulcerative-erosive processes of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as a violation of the functionkidneys and liver. Therefore, patients who take NSAIDs for a long time need drugs that protect the gastric mucosa and regular laboratory control of the liver and kidneys.
Systemic muscle relaxants, i. e. Drugs that relieve muscle spasm. The principle of their action lies in the title: relaxation of spasmodic muscles helps to reduce compression of nerves and blood vessels, edema in the damage zone - blood circulation and innervation improves - pain decreases; Due to the decrease in muscle defense, the voltage of the ligamentous apparatus decreases - the stab (protrusion) of the intervertebral disc decreases - pain subsides, the volume of movements increases.
Local anesthetics Or drugs for local anesthesia are used for drug treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis in the form of the so -called paravertebral blockade, when the medicine solution is administered first subcutaneously, and then into the process of processes of the affected vertebra in the projection of the alleged compression of the nerve root. When accumulating in the membranes of the nerve fibers, the drug effectively blocks the pain signal. Therapist will certainly not be able to perform such a blockade; for its conduct, it is necessary to contact a neurologist or neurosurgeon.
Also, for paravertebral administration, sometimes used Glucocorticosteroid solutions (GKS) - hormonal drugs with a pronounced anti -inflammatory effect. Their local application allows you to achieve maximum effect when minimizing the risk of undesirable side effects of the drug. Such blockade are carried out courses 2-3 times a year, a neurologist or neurosurgeon doctor should perform them.
B vitamins "B". In any pharmacy you can find a variety of drugs of this group, both in forms for oral administration and for intramuscular administration. It is believed that they have a neurotrophic and mild analgizing effect, however, a reliable justification for their use for osteochondrosis of the spine has not been obtained by evidence -based medicine.
Physiotherapy for osteochondrosis of the lumbar
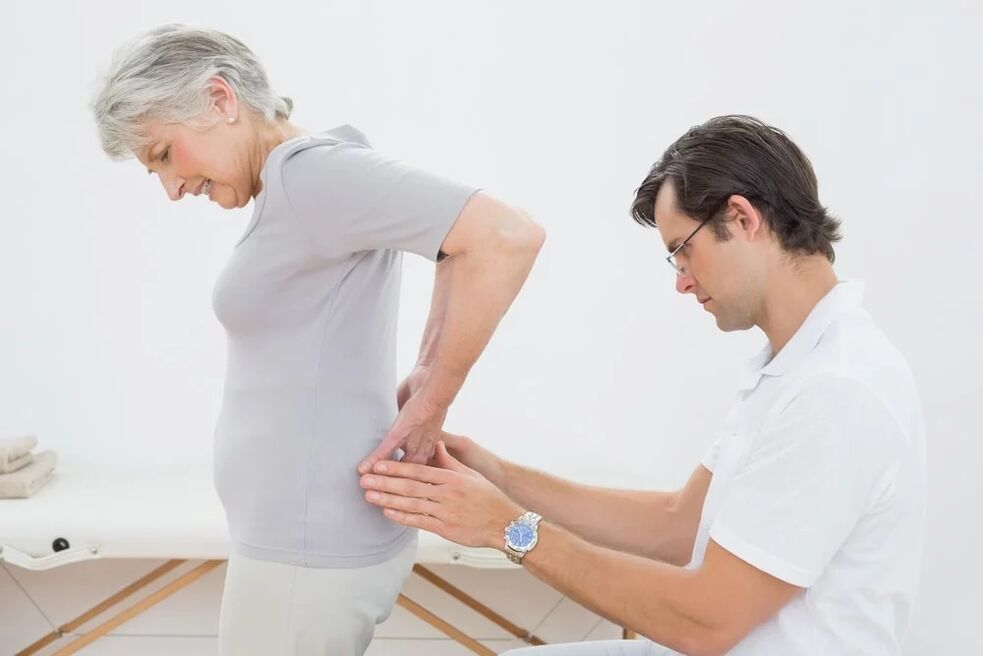
Unfortunately, sometimes comprehensive treatment using modern medicines, physiotherapy, massage and exercise therapy is ineffective - a person continues to experience pain, restriction of physical activity remains, and the quality of life suffers significantly. This happens in the later stages of the disease, when volumetric, often multiple hernias of intervertebral discs are formed. In such a situation, surgical treatment is shown. In addition, surgery is indicated with the so -called "decay of a hernia", when a significant compression of the spinal canal causes uncompanying pain, statodynamic disorders and blockade of the function of the bladder and intestines. In such cases, the operation is carried out on an emergency order. The purpose of surgical interventions for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is the mechanical decompression of the spinal canal and nerve roots.
Currently, both long -known volumetric surgical methods are used in the surgical treatment of osteochondrosis and minimally invasive endoscopic interventions proposed by modern medicine using laser and radio frequency effects, some of which can be carried out even under local pain relief. Having examined the main methods of treating osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, I would like to once again note that the patient asking the question "how to cure lumbar osteochondrosis? " Should rely not only for the help of doctors, but also on his own forces, understanding the significance of a healthy lifestyle, in which proper dose and mainly dosed physical activity is welcomed, and most importantly, a branch of in is present. Victory over the disease.